Theme: Navigating the Future of Pharmacology and Ethnomedicine
Ethnopharmacology 2018
Conference Series LLC Ltd is a renowned organization that organizes highly notable pharmaceutical conferences throughout the globe. After a successful conference of Ethnopharmacology 2017, Conference Series LLC Ltd is currently bringing forth "11th International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmacology and Ethnopharmacology" (Ethnopharmacology 2018) slated on July 18-19, 2018 at Atlanta, USA.
Ethnopharmacology 2018 covers various aspects of Pharmacology, Ethnopharmacology, Ethnopharmacology of Medicinal Plants, Latest Trends in Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemical Studies of Plants and Plant Extracts, Pharmacognosy, Herbal and Holistic medicine, Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),Traditional Korean medicine, Traditional Japanese Medicine, Acupuncture and moxibustion, Intercultural Ethnopharmacology, Advancements in Ayurveda and Unani, Natural Products in Clinical Pharmacology, Phytochemistry and Phytopharmaceuticals ,Entrepreneurs Investment Meet
Track 1: Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of science worried with the investigation of medication action, where a medication can be extensively characterized as any man-made, characteristic, or endogenous (from inside body) atom which applies a biochemical and additionally physiological impact on the cell, tissue, organ, or living being (some of the time the word pharmacon is utilized as a term to envelop these endogenous and exogenous bioactive species). All the more particularly, it is the investigation of the associations that happen between a living life form and chemicals that influence typical or anomalous biochemical capacity. In the event that substances have therapeutic properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals.
Track 2: Ethnopharmacology
Ethnopharmacology is a study or comparison of the traditional medicine practiced by various ethnic groups, and especially by indigenous peoples. The word ethnomedicine is sometimes used as a synonym for traditional medicine. Ethnomedical research is interdisciplinary; in its study of traditional medicines, it applies the methods of ethnobotany and medical anthropology. Often, the medicine traditions it studies are preserved only by oral tradition.
Scientific ethnomedical studies constitute either anthropological research or drug discovery research. Anthropological studies examine the cultural perception and context of a traditional medicine. The purpose of drug discovery research is to identify and develop a marketable pharmaceutical product.
Track 3: Ethnopharmacology of Medicinal Plants
Ethnopharmacology of Medicinal Plants is the field of drug discovery from plants and offers stimulating, thoughtful, and critical information that should contribute in some way to the scientific progress of ethnopharmacology and to the discovery of drugs.
It emphasizes the fundamental importance of the precise observation of the use of each medicinal plant, combined with pharmacological experiments and its botanical classification, and provides the base for a new theory of ethnopharmacology
Track 4: Latest Trends in Ethnopharmacology
Ethnopharmacology has already played important role in the development of conventional medicine and is likely to play more significant role in the years to come. A team work amongst ethnobotanists, ethnopharmacologists, physicians and phytochemists is essential for the fruitful outcome on medicinal plants research. While the ethnopharmacologists have a greater role to play in the rationalization of combination of activities, the phytochemist's role will slightly shift towards standardization of botanicals.
Track 5: Phytochemical Studies of Plants and Plant Extracts
The plant kingdom is a treasure house of potential drugs and in the recent years there has been an increasing awareness about the importance of medicinal plants. Drugs from the plants are easily available, less expensive, safe, and efficient and rarely have side effects. The plants which have been selected for medicinal use over thousands of years constitute the most obvious choice of examining the current search for therapeutically effective new drugs such as anticancer drugs antimicrobial drugs anti hepatotoxic compounds.
According to World Health Organization (WHO), medicinal plants would be the best source to obtain variety of drugs. About 80% of individuals from developed countries use traditional medicines, which has compounds derived from medicinal plants. However, such plants should be investigated to better understand their properties, safety, and efficiency. Medicinal plants contain some organic compounds which provide definite physiological action on the human body and these bioactive substances include tannins, alkaloids, carbohydrates, terpenoids, steroids and flavonoids. These compounds are synthesized by primary or rather secondary metabolism of living organisms. Secondary metabolites are chemically and taxonomically extremely diverse compounds with obscure function. They are widely used in the human therapy, veterinary, agriculture, scientific research and countless other areas.
Track 6: Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicines or crude drugs produced from natural sources such as plants, microbes, and animals. It includes analysis of their biological, chemical, biochemical, and physical properties. The renaissance of herbal medicine in this country creates a demand for studies in the field of Pharmacognosy. From a practical perspective this includes:
quality control (identity, purity, consistency)
efficacy (therapeutic indications, clinical studies, pharmacological investigations)
safety (adverse reactions, drug interactions, contraindications, precautions)
Track 7: Herbal and Holistic Medicine
Herbal medicine, also called botanical medicine or phytomedicine, refers to using a plant's seeds, berries, roots, leaves, bark, or flowers for medicinal purposes. Herbalism has a long tradition of use outside conventional medicine. It is becoming more mainstream as improvements in analysis and quality control, along with advances in clinical research, show the value of herbal medicine in treating and preventing disease.
Holistic medicine is a system of health care which fosters a cooperative relationship among all those involved, leading towards optimal attainment of the physical, mental emotional, social and spiritual aspects of health. It emphasizes the need to look at the whole person, including analysis of physical, nutritional, environmental, emotional, social, spiritual and lifestyle values. It encompasses all stated modalities of diagnosis and treatment including drugs and surgery if no safe alternative exists. Holistic medicine focuses on education and responsibility for personal efforts to achieve balance and well-being.
Track 8: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) originated in ancient China and has evolved over thousands of years. TCM practitioners use herbal medicines and various mind and body practices, such as acupuncture and tai chi, to treat or prevent health problems. In the United States, people use TCM primarily as a complementary health approach.
TCM encompasses many different practices, including acupuncture, moxibustion (burning an herb above the skin to apply heat to acupuncture points), Chinese herbal medicine, tui na (Chinese therapeutic massage), dietary therapy, and tai chi and qi gong (practices that combine specific movements or postures, coordinated breathing, and mental focus)
Track 9: Traditional Korean Medicine
Traditional Korean medicine refers to the traditional medicine practices that developed in Korea. Traditional Korean medicine, which has been in existence since antiquity, is based on Eastern philosophy and was developed through medical exchanges between countries that use Chinese characters, such as China and Japan. In Traditional Korean medicine, the human body is viewed as a miniature universe. The principles, treatment methods and medication for the physiology and pathology of the body are explained by the yin-yang and five elements theory, which is based on the concept of yin and yang as the operating principle of the universe. Therefore, illnesses are not treated and cured locally; rather, they are regarded as the result of an abnormality or change to the entire body and are, therefore, treated holistically.
Track 10: Traditional Japanese Medicine
Kampo (or Kanpo) is a traditional Japanese therapeutic system, the bulk of which is derived from the classical Chinese medicine that came to Japan in the 5th and 6th centuries. Over the years, the Japanese have created unique diagnosis methods, herbal formulas, and therapeutic approaches. Kampo includes most of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) modalities including acupuncture, moxibustion (heat therapy), Anma (or Tuina, an ancient massage technique and the basis of Shiatsu therapy), diet, and herbal medicine.
Track 11: Acupuncture and Moxibustion
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body. It is a key component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). TCM theory and practice are not based upon scientific knowledge, and acupuncture is a pseudoscience. There are a diverse range of acupuncture theories based on different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country. The method used in TCM is likely the most widespread in the US. It is most often used for pain relief, though it is also used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is generally used only in combination with other forms of treatment.
Moxibustion is a form of heat therapy in which dried plant materials called "moxa" are burned on or very near the surface of the skin. The intention is to warm and invigorate the flow of Qi in the body and dispel certain pathogenic influences. Moxa is usually made from the dried leafy material of Chinese mugwort (Artemesia argyi or A.vlugaris), but it can be made of other substances as well.
Moxibustion is used for: Pain due to injury or arthritis, especially in "cold" patterns where the pain naturally feels better with the application of heat, Digestive problems and irregular elimination, Gynecological and obstetrical conditions, including breech presentation in late term pregnancy and Protection against cold and flu strains.
Track 12: Botanical drug
“Botanical drug” is a form of finished product containing ingredients and or constituents of vegetable matter. The classification includes whole plants or plant parts and also include algae or macroscopic fungi. A botanical must undergo identification and taxonomic classification. The most important step of the process and, for botanicals, the most difficult step to satisfy is FDA’s review and acceptance of the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC). Drug if it is intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, or treatment of disease in humans. Botanical drug products often have unique features.
Conference Series LLC Ltd is a renowned organization that organizes highly notable pharmaceutical conferences throughout the globe. Conference Series LLC Ltd is currently bringing forth "11th International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmacology & Ethnopharmacology” (Ethnopharmacology 2018) slated on July 18-19, 2018 Atlanta, USA.
Conference Series LLC Ltd Organizes 3000+ Global Events Every Year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and Publishes 700+ Open access Journals which contains over 70000 eminent personalities as editorial board members as reputed scientists and 1200+ Symposiums & Workshops. To know more about the conference series LLC Ltd
Ethnopharmacology 2018 conveys recent developments in Pharmacology and Ethnopharmacology. A complete knowledge of a scientific discipline that described the overt effects of biologically active chemicals, pharmacology now explores the molecular mechanisms by which drugs cause biological effects. In the broadest sense, pharmacology is the study of how chemical agents, both natural and synthetic (i.e., drugs) affect biological systems.
Ethnopharmacology involves a wide range of scientists from varying specialties. The practices and public interest in natural therapies, namely herbal medicine, have been increased dramatically throughout the world. This has increased the international trade in herbal medicine enormously. A paradigm shift is observed in the use of natural product based medicine for the management of health care, which can significantly impart a major task in economic growth.
Knowledge about traditional drugs/medicines is put into practice in different cultural settings in daily health care, nutrition, veterinary, hunting, pest control etc. We are interested in the perception and the interface of the emic and ethic perspective of such knowledge and we encourage and promote the future use of such local and traditional knowledge.
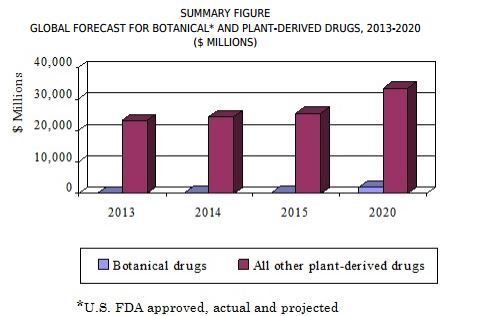
Botanical and Plant-Derived Drugs: Global Markets
The global market for botanical and plant-derived drugs was valued at $23.2 billion in 2013 and $24.4 billion in 2014. This total market is expected to reach $25.6 billion in 2015 and nearly $35.4 billion in 2020, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2015 to 2020.
Target Audience:
â— The pharmaceutical industry, especially companies supplying bulk or formulated plant- derived drugs or companies that are planning to enter this field.
â— Medical research institutions.
â— International organizations and governmental organizations with relevant responsibilities such as health, drug safety, conservation and the environment, and foreign trade.
â— Investors.
â— The financial and analyst community.
Source: BCC Research
Conference Highlights
- Pharmacology and Drug Design
- Ethnopharmacology and Ethnomedicine
- Phytochemical Studies of Medicinal Plants and Plant Extracts
- Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy
- Herbal and Holistic medicine
- Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
- Entrepreneurs Investment Meet
- Natural Products Research
- Phytochemistry and Phytopharmaceuticals
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Botanical Drug
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 18-19, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pharmacology
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: Open Access
- Biochemistry & Pharmacology: Open Access
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by